Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial lung disease related to systemic autoimmune myopathies: a narrative review
Accepted: 5 April 2023
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
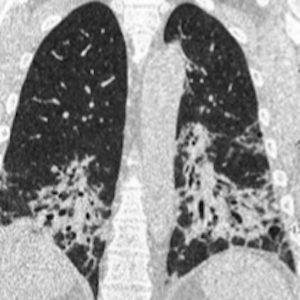
Systemic autoimmune myopathies (SAMs) are rare diseases that lead to muscle inflammation and may be associated with a variety of systemic manifestations. Although there is great heterogeneity in the spectrum of extra-muscular involvement in SAMs, interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most frequent lung manifestation. SAM-related ILD (SAM-ILD) presents significant variations according to geographic location and temporal trends and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Several myositis autoantibodies have been discovered over the last decades, including antibodies targeting aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes, which are associated with a variable risk of developing ILD and a myriad of other clinical features. In this review, the most relevant topics regarding clinical manifestations, risk factors, diagnostic tests, autoantibodies, treatment, and prognosis of SAM-ILD are highlighted. We searched PubMed for relevant articles published in English, Portuguese, or Spanish from January 2002 to September 2022. The most common SAM-ILD patterns are nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and organizing pneumonia. The combination of clinical, functional, laboratory, and tomographic features is usually sufficient for diagnostic confirmation, without the need for additional invasive methods. Glucocorticoids remain the first-line treatment for SAM-ILD, although other traditional immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine, mycophenolate, and cyclophosphamide have demonstrated some efficacy and, therefore, have an important role as steroid-sparing agents.
Supporting Agencies
This work was supported by Brazilian Society of RheumatologyHow to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
Similar Articles
- S. Zingarelli, P. Airò, M. Frassi, C. Bazzani, M. Scarsi, M. Puoti, Prophylaxis and therapy of HBV infection in 20 patients treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs or with biological agents for rheumatic diseases , Reumatismo: Vol. 60 No. 1 (2008)
- P. Marson, G. Pasero, L. Punzi, G. Zanchin, On the main stages of the history of intra-articular therapy , Reumatismo: Vol. 59 No. 3 (2007)
- G. Leardini, M.T. Mascia, S. Stisi, G. Sandri, M. Franceschini, Sanitary costs of osteoarthritis , Reumatismo: Vol. 53 No. 4 (2001)
- T. Maio, P. Trezzi, M.A. Cimmino, Pure analgesics in a rheumatological outpatient clinic , Reumatismo: Vol. 53 No. 2 (2001)
- L. Cavagna, P. Rossi, L. Bogliolo, E. Antoniazzi, C. Gelmi, R. Caporali, C. Montecucco, Early electroretinografic changes in elderly RA patients treated with hydroxychloroquine , Reumatismo: Vol. 54 No. 3 (2002)
- A. Hoxha, A. Ruffatti, P. Grypiotis, M. Podswiadek, C. Botsios, U. Fiocco, L. Punzi, S. Todesco, Antinuclear, anti-dsDNA and anti-ENA antibodies in patients affected with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis during treatement with infliximab , Reumatismo: Vol. 58 No. 2 (2006)
- A. Colangelo, F. Tromby, G. Cafaro, R. Gerli, E. Bartoloni, C. Perricone, Vasculitis associated with adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency: at the crossroads between Behçet’s disease and autoinflammation. A viewpoint , Reumatismo: Vol. 75 No. 3 (2023)
- A. Cossu, P.A. Cossu, A. Carcassi, Chronic polyarthritis in a patient affected by sarcoidosis and chronic HCV infection. Case report and review of the literature , Reumatismo: Vol. 54 No. 2 (2002)
- M. Rossini, F.P. Cantatore, A. Del Puente, B. Frediani, D. Gatti, S. Giannini, M. Varenna, O. Viapiana, G.D. Sebastiani, Expert opinion on the management of patients with osteoporosis with anabolic drugs in Italy , Reumatismo: Vol. 76 No. 2 (2024)
- G. Brambilla, A. Brucato, Y. Adler, M. Bosetti, P. Coppini, A. Caforio, D. Spodick, B. Canesi, Recurrent acute idiopathic pericarditis: rheumatologic therapy, autoantibodies and long term outcome , Reumatismo: Vol. 59 No. 1 (2007)
<< < 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 > >>
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/reumatismo.2023.1571
https://doi.org/10.4081/reumatismo.2023.1571




