Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Serum klotho concentrations inversely correlate with the severity of nailfold capillaroscopic patterns in patients with systemic sclerosis
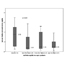
Klotho is a transmembrane and soluble glycoprotein that governs vascular integrity. Previous studies have demonstrated reduced serum klotho concentrations in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), and it is known that klotho deficiency can impair the healing of digital ulcers related to microvessel damage. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between serum klotho levels and nailfold capillaroscopic abnormalities in SSc patients. We retrospectively enrolled 54 consecutive patients with SSc diagnosed on the basis of the 2013 EULAR/ACR criteria [11 with diffuse SSc; 47 females; median age 68.0 years (IQ 18); median disease duration 11.0 years (IQ 7)]. Serum klotho concentrations were determined by means of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. On the basis of the 2000 classification of Cutolo et al., 14 patients had normal nailfold capillaroscopic findings, 8 had an early scleroderma pattern, 21 an active scleroderma pattern, and 11 a late scleroderma pattern. The median serum klotho concentration was 0.29 ng/mL (IQ 1). Regression analysis of variation showed an inverse correlation between serum klotho concentrations and the severity of the capillaroscopic pattern (p=0.02; t -2.2284), which was not influenced by concomitant treatment. Logistic regression did not reveal any significant association between the risk of developing digital ulcers and nailfold capillaroscopic patterns, serum klotho levels, or concomitant medications. The presence of avascular areas significantly correlated with calcinosis (p=0.006). In line with previous studies, our findings confirm that klotho plays a role in preventing microvascular damage detected with nailfold capillaroscopy.
Downloads
How to Cite
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/reumatismo.2019.1129
https://doi.org/10.4081/reumatismo.2019.1129